Delving into eco-friendly architecture, this introduction immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative. From defining the concept to discussing its key features and benefits, this overview sets the stage for a deeper exploration of sustainable building practices.
As we journey through the world of eco-friendly architecture, we uncover the innovative designs, case studies, and FAQs that shed light on the importance of sustainable construction in today's world.
Definition of Eco-Friendly Architecture

Eco-friendly architecture is a design approach that aims to create buildings and structures that are environmentally responsible and resource-efficient throughout their life cycle. This type of architecture focuses on reducing the negative impact on the environment while enhancing the well-being of the occupants.The principles behind eco-friendly architecture include using sustainable materials, maximizing energy efficiency, minimizing waste, and integrating natural elements into the design.
By adopting these principles, eco-friendly buildings can help reduce carbon footprint, conserve resources, and promote a healthier living environment.
Examples of Eco-Friendly Materials Used in Architecture
- Bamboo: A fast-growing renewable resource that can be used for flooring, furniture, and even structural elements in buildings.
- Recycled Glass: Glass from old windows or bottles can be repurposed for countertops, tiles, and insulation material.
- Reclaimed Wood: Salvaged wood from old buildings or structures can be used for flooring, paneling, and furniture, reducing the need for new timber.
- Solar Panels: Photovoltaic panels can be integrated into the design of a building to harness solar energy and reduce reliance on traditional power sources.
- Green Roofs: Living roofs with vegetation help reduce heat absorption, improve insulation, and promote biodiversity in urban areas.
Benefits of Eco-Friendly Architecture
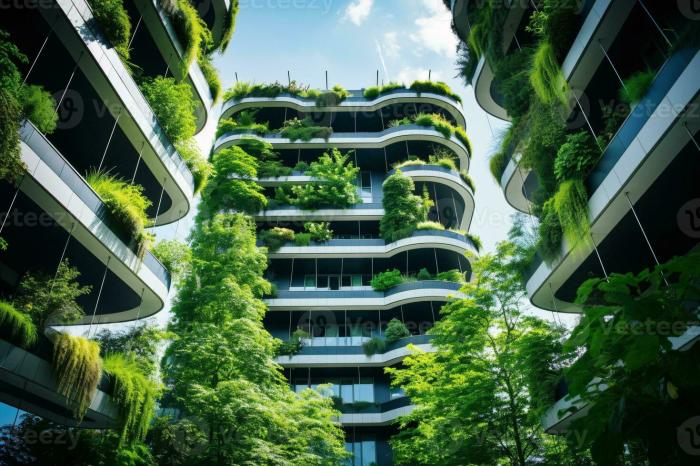

Eco-friendly architecture offers a wide range of benefits that extend beyond just the physical structures themselves. From environmental advantages to economic savings and social impacts, incorporating sustainable practices in architectural design can lead to a more sustainable future for all.
Environmental Benefits
- Reduced carbon footprint: Eco-friendly buildings utilize sustainable materials and energy-efficient systems, resulting in lower greenhouse gas emissions.
- Conservation of natural resources: By using renewable materials and efficient designs, eco-friendly architecture helps preserve natural resources like water, energy, and forests.
- Improved air and water quality: Green buildings often incorporate features that enhance indoor air quality and reduce water consumption, contributing to a healthier environment for occupants and surrounding ecosystems.
Economic Advantages
- Long-term cost savings: While initial construction costs of eco-friendly buildings may be higher, the long-term savings on energy bills and maintenance expenses can outweigh the upfront investment.
- Increased property value: Green buildings are often more attractive to buyers and tenants, leading to higher property values and rental rates in the long run.
- Government incentives: Many governments offer financial incentives, tax credits, or grants for eco-friendly building projects, further reducing costs for developers and owners.
Social Impact
- Healthier living spaces: Eco-friendly buildings prioritize the health and well-being of occupants, providing a comfortable and sustainable environment that promotes physical and mental well-being.
- Community engagement: Sustainable architecture projects often involve local communities in the planning and design process, fostering a sense of ownership and pride in the built environment.
- Educational opportunities: Green buildings serve as educational tools, raising awareness about sustainability and inspiring future generations to prioritize eco-friendly practices in their own lives.
Key Features of Eco-Friendly Buildings
Eco-friendly buildings are designed with specific features that prioritize sustainability, energy efficiency, and environmental responsibility. These key features play a crucial role in reducing the carbon footprint of buildings and promoting a healthier environment for occupants.
Importance of Energy-Efficient Systems
Energy-efficient systems are essential in eco-friendly architecture as they help minimize energy consumption and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Features such as solar panels, LED lighting, smart thermostats, and efficient insulation contribute to lower energy bills and a smaller environmental impact.
Use of Sustainable Materials
The use of sustainable materials in construction is another key feature of eco-friendly buildings. Materials such as bamboo, recycled steel, reclaimed wood, and low-VOC paints are environmentally friendly alternatives that help reduce waste and promote a healthier indoor environment. By choosing sustainable materials, builders can contribute to the conservation of natural resources and reduce the overall environmental impact of construction projects.
Innovative Designs in Eco-Friendly Architecture
Innovative designs play a crucial role in promoting sustainability in architecture by incorporating environmentally friendly features. These designs not only reduce the negative impact on the environment but also create healthier and more efficient living spaces for occupants.
Integration of Green Spaces and Natural Light
The integration of green spaces and natural light is a key aspect of eco-friendly architecture. Green roofs, vertical gardens, and atriums are some innovative designs that help bring nature into urban environments. These features not only improve air quality and provide insulation but also create a visually appealing and calming environment for building occupants.
Additionally, maximizing natural light through strategically placed windows, skylights, and light shelves reduces the need for artificial lighting, decreasing energy consumption and creating a more comfortable indoor environment.
Zero-Energy Buildings and Design Principles
Zero-energy buildings are another innovative design trend in eco-friendly architecture. These buildings are designed to produce as much energy as they consume, typically through renewable sources such as solar panels, wind turbines, and geothermal systems. Design principles for zero-energy buildings include optimizing insulation, using energy-efficient appliances, incorporating passive solar design, and implementing advanced HVAC systems.
By combining these principles, zero-energy buildings can achieve a net-zero energy balance, significantly reducing their carbon footprint and operating costs.
Case Studies of Eco-Friendly Architectural Projects
Examining successful eco-friendly architectural projects from various parts of the world provides valuable insights into sustainable building practices.
1. The Edge, Amsterdam
The Edge in Amsterdam is considered one of the most sustainable office buildings in the world. It utilizes innovative technologies such as smart sensors to optimize energy consumption and promote a healthy work environment. Challenges faced during construction included integrating complex systems for energy efficiency and ensuring a balance between natural light and artificial lighting.
Solutions implemented included the use of solar panels, advanced insulation materials, and a green roof to reduce energy usage. The impact of The Edge on the environment and society is significant, as it sets a precedent for sustainable office design and encourages other companies to prioritize eco-friendly practices.
2. One Central Park, Sydney
One Central Park in Sydney is a mixed-use development that showcases a unique approach to integrating green spaces within urban environments. The project faced challenges in designing vertical gardens and incorporating natural elements into the architecture. Solutions included the use of hydroponic systems for plant growth, automated sun shading to regulate temperature, and rainwater harvesting for irrigation.
This project has had a positive impact on the local community by providing a green oasis in the city and promoting biodiversity within the urban landscape.
3. Masdar City, Abu Dhabi
Masdar City in Abu Dhabi is a planned sustainable community that aims to be carbon-neutral and zero-waste. The project faced challenges in implementing renewable energy sources and creating a walkable urban environment in a desert climate. Solutions included the use of solar power, wind turbines, and efficient public transportation systems.
The impact of Masdar City extends beyond its boundaries, serving as a model for sustainable urban development and inspiring similar initiatives around the world.
Ultimate Conclusion
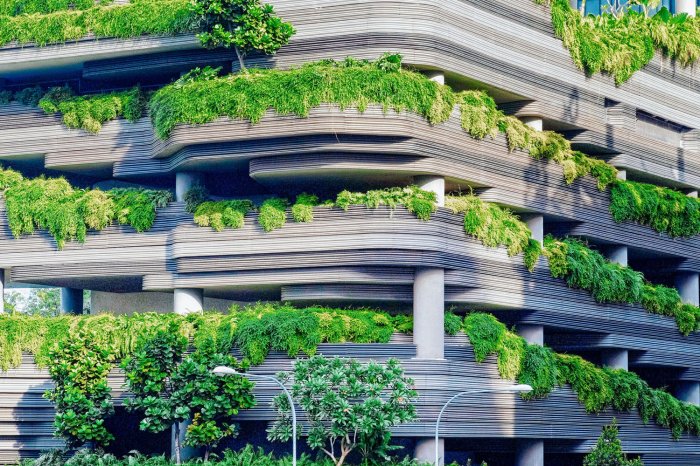

In conclusion, eco-friendly architecture is not just a trend but a crucial step towards a greener and more sustainable future. By embracing eco-friendly practices, we can create buildings that not only benefit the environment but also enhance our quality of life.
FAQ Corner
What is the importance of energy-efficient systems in eco-friendly architecture?
Energy-efficient systems reduce energy consumption, lower utility costs, and minimize environmental impact, making them essential components of eco-friendly buildings.
How do sustainable materials contribute to eco-friendly construction?
Sustainable materials are renewable, non-toxic, and energy-efficient, promoting healthier indoor environments and reducing the ecological footprint of buildings.
What are some challenges faced in implementing eco-friendly architectural projects?
Challenges include higher initial costs, limited availability of materials, and the need for specialized knowledge in sustainable design and construction.